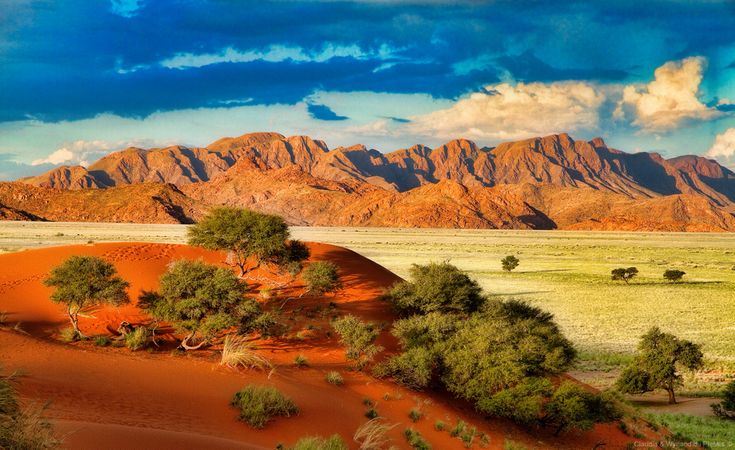
Namibia, a country in southern Africa known for its dramatic deserts, wildlife and cultural diversity, has recently drawn global attention for both its political developments and economic progress. Bordering Angola, Zambia, Botswana, South Africa and the Atlantic Ocean, Namibia is one of the least densely populated countries in the world, giving it vast open landscapes and a unique environmental identity.
The country’s geography, marked by the Namib Desert, national parks and coastal regions, continues to shape its economy and global image. At the same time, recent political changes and ongoing development challenges are placing Namibia firmly in international conversations.
Historic Political Moment
Namibia made history with the election of Netumbo Nandi-Ndaitwah as the country’s first woman president. The development is widely seen as a milestone for political representation and women’s leadership in Africa. Analysts view the move as a sign of gradual political transformation and growing inclusivity within the country’s democratic framework.
The election has also highlighted Namibia’s stable governance model, which has remained consistent since independence and continues to attract global attention.
Economy Driven by Resources and Tourism
Namibia’s economy is largely supported by mining, agriculture and tourism. The country is rich in natural resources, particularly diamonds and uranium, which contribute significantly to national revenue. These sectors have long formed the backbone of Namibia’s economic structure.
Tourism plays an equally important role. Visitors from across the world travel to Namibia to experience its natural beauty and wildlife. Destinations such as the Namib Desert, Etosha National Park and the Skeleton Coast attract international travellers and contribute to local employment. Following the pandemic slowdown, tourism activity has gradually recovered, supporting communities and small businesses.
Social and Environmental Challenges
Despite progress, Namibia faces several structural challenges. Unemployment remains a concern, especially among young people. Income inequality and limited economic opportunities in rural areas continue to affect livelihoods.
Climate change has added further pressure. Drought conditions and water scarcity have impacted agriculture and daily life, making environmental sustainability a major policy priority. These issues highlight the balance Namibia must maintain between development and resource management.
Conservation and Global Recognition
Namibia is also widely recognised for its conservation efforts. The country has taken significant steps to protect wildlife and natural habitats, becoming a global example of community-based conservation models. These initiatives support biodiversity while also generating economic benefits through eco-tourism.
International organisations and environmental groups often cite Namibia’s approach as a model for sustainable development in ecologically sensitive regions.
Looking Ahead
Namibia’s journey reflects the complex realities faced by many developing nations. Political progress, economic potential and environmental responsibility are shaping the country’s future direction. While challenges remain, stable governance, global partnerships and continued conservation efforts position Namibia for steady growth.
As the nation moves forward, its experience highlights how development, sustainability and social progress must work together. Namibia’s story is not only about its deserts and wildlife, but also about its evolving role in global politics and economic change.